| Learning Aims: |
|
| Materials: |
|
| Suggestions for use: |
|
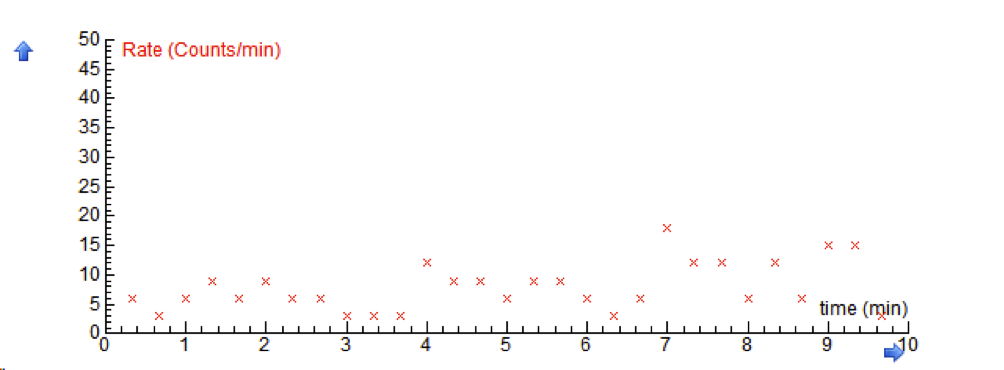
Here students learn to which radiations people are exposed, how an annual radiation dose is calculated and what are effects of radiation on humans. In activity 1 students analyse the sources of ionising radiation on Earth. Ionising radiation in our direct environment arises from natural processes (e.g. cosmic radiation, radioactivity in the body, inhalation of radon gas, radionuclides in food and drink) and from artificial process (such as medical X-rays, fallout from nuclear weapons tests, and discharges of radioactive waste). In activity 2 students investigate the radiation of their environment, they measure background radiation in different places and measure the radiation of some natural materials. In this activity they observe the random nature of the radiation process.
In activity 3 they learn how absorbed radiation doses by the human body are calculated and in which units they are measured. http://www.epa.gov/rpdweb00/understand/calculate.html In activity 5 the students find out and discuss the effects of radiation on the human body and cells. |
| Possible questions: |
|