| Learning Aims: |
|
| Materials: |
|
| Suggestions for use: |
|
Here students focus on the process of radioactive decay. In activity 1 students simulate the process of radioactive decay and learn that it is a random process. In activity 2 they explore a given radioactive decay model and determine the function, which describes the radioactive decay. In activity 3 the radioactive decay law, the decay constant and the half-life time are introduced. In activity 4 students measure the activity of a radioactive isotope. Based on the measured results they determine the decay constant and calculate the half-life value. The short-lived radioisotope Ba-137m is very suitable for measuring and by using a Cs-137/Ba-137m Isotope Generator easy to make. The isotope generator Barium 137m contains Cesium-137 as the long parent nuclide, which has a half-life of 30.25 years. Cs137 decays, by emission of beta radiation, into stable isotope Ba137. This transition is partly affected (approx. 5%) by direct conversion into stable isotope Ba137 and partly (95%) via the metastable energy state of Ba137m. In the experiment Ba is “milked” out of the Isotope Generator by pressing eluting solution through the generator.
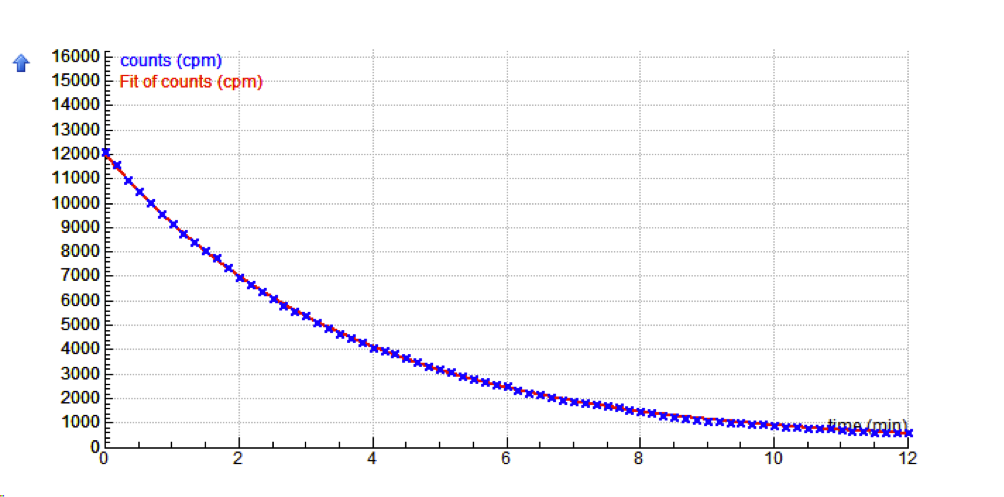
Exemplary data of the Barium-137m radioactive decay: measurement with MoLab data-logger and ML26m Radiation sensor, the coefficient of exponential function is l = 0.272, the half-time t1/2= ln2/l=0.6931/0.272=2.548 min. In activity 5, students modify the model of activity 2 to create a model of radioactive decay of the isotope used in their experiment and compare the model data with the experimental results. |
| Possible questions: |
|