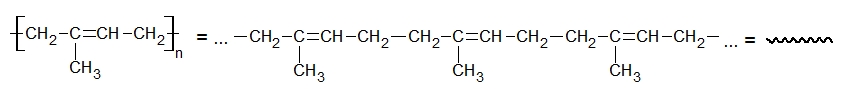| Learning Aims: |
|
| Materials: |
|
| Suggestions for use nad possible questions: |
|
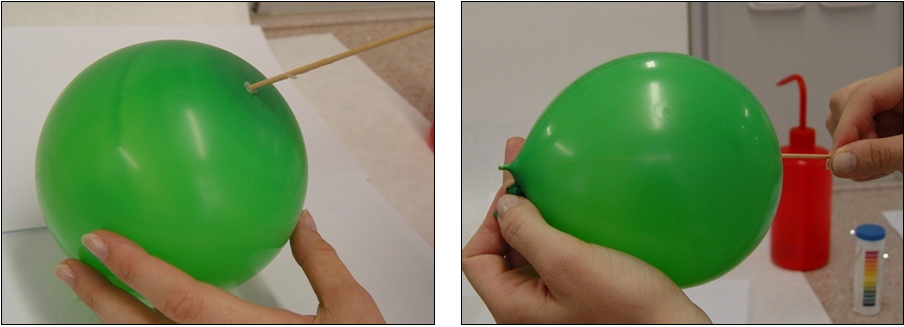
Task: Try to pull a skewer through the balloon without an immediate burst. On the basis of your knowledge about the structure (e.g. found in the Internet), try to explain the behaviour and properties of polymer Procedure:
Discussion: Explain the balloon behaviour, why it bursts in one case but why in principle it is possible to draw the skewer through. Due to lower tension of the balloon near the top and the knot, it is possible to pull the skewer through the balloon without damaging it since the structure of polymer is not affected by the rupture of chains but only by their extension. During a “rougher“ use of the skewer, there occurs a rupture of the polymer chains, and the balloon bursts. Forces acting on the reinforced polymers therefore influence their properties and possibilities of use. The balloon is made from the material, which is called a reinforced polymer. I.e. that the polymeric chains, which are formed by macromolecules of a linear chain consisting of repetitive units linked by a covalent bond, are further grouped together to form a multidimensional structure.
Linear polymer
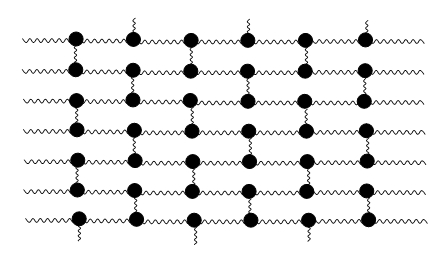
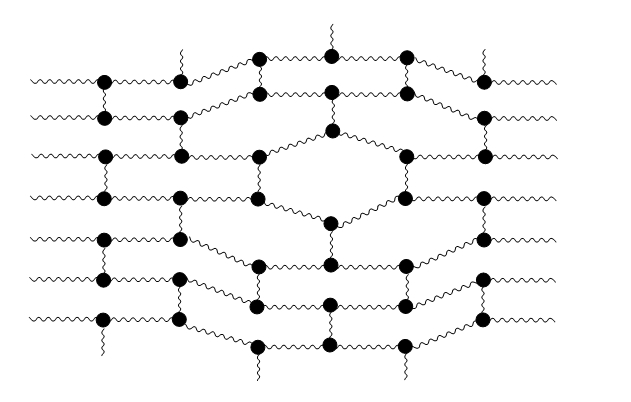
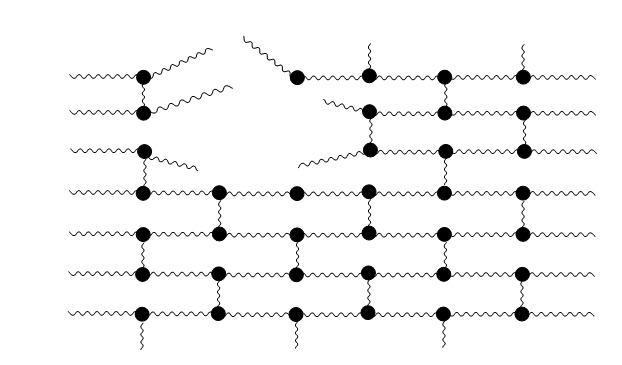
Reinforced polymer This bond keeps the polymer molecules connected and allows the polymer extension up to a certain point where the force or tension on the lateral ligaments is to high and it leads to their breaking and the rupture of the polymer.
After extension of reinforced polymer
After rupture of reinforced polymer Experience from implementation: the balloon should be inflated in the way that will allow its diameter being smaller than 10 cm (or in other words, shorter than the length of the skewer). The skewer should be pulled through very carefully.
a) Skewer through the balloon wall b) Slow rotation of the skewer to penetrate through the wall
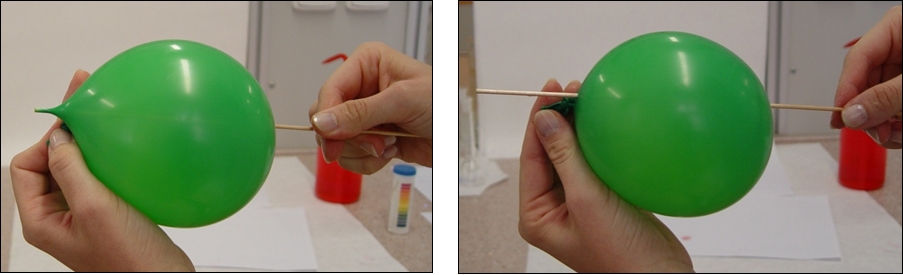
c) Skewer passage through the balloon wall d) Skewer through the balloon
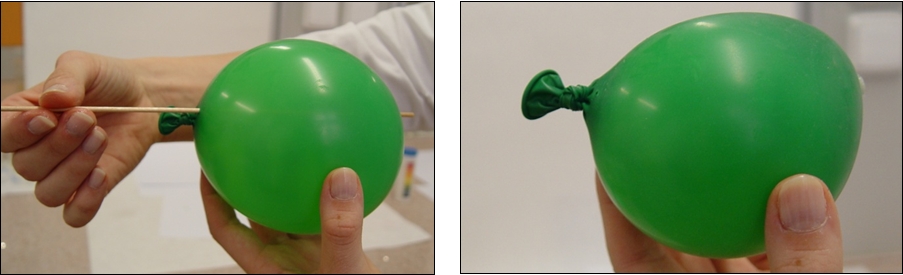
e) Removing the skewer out of the balloon f) After the passage of the skewer the balloon slowly leaks |