Determination of the maximum power of the constructed device.
The power P, of the cell is equal the product of voltage U and current I from the external circuit:
P = U · I
Knowledge of this characterictic enables determination of the maximum power that can be taken from the cell. On the other hand, the ratio of this power to the intensity of light falling on the cell gives the efficiency of solar energy conversion into electricity.
Engaging questions:
- How can the current intensity be influenced?
- What parameters should be fixed in subsequent measurements?
Equipment:
- Solar cell (from Activity 3a),
- Decade resistors: R=10 kΩ, R=1000 Ω , R=100 Ω, (multimeters with variable resistance may be used),
- multimeter (ammeter),
- cables for connection.
Students can design the system for measuring the dependence of the voltage on the current intensity by themselves. The exemplary system is presented in Figure 3. Resistance may be changed in the range of 100 Ω -10000 Ω
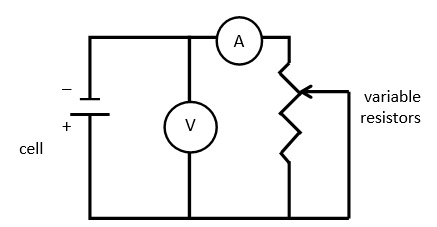
Figure IV.10. A diagram of a circuit for the measurement of the voltage-current characteristic.
Table IV.1. Exemplary results:
|
U [mV] |
I [mA] |
R [W] |
P [mW] |
|
355 |
0,038 |
11100 |
13,490 |
|
331 |
0,040 |
9100 |
13,240 |
|
303 |
0,048 |
7100 |
14,544 |
|
269 |
0,056 |
5100 |
15,064 |
|
214 |
0,075 |
3100 |
16,050 |
|
116 |
0,110 |
1100 |
12,760 |
|
101 |
0,115 |
900 |
11,615 |
|
84 |
0,123 |
700 |
10,332 |
|
64 |
0,130 |
500 |
8,320 |
|
30 |
0,145 |
300 |
4,350 |
|
4 |
0,155 |
10 |
0,620 |
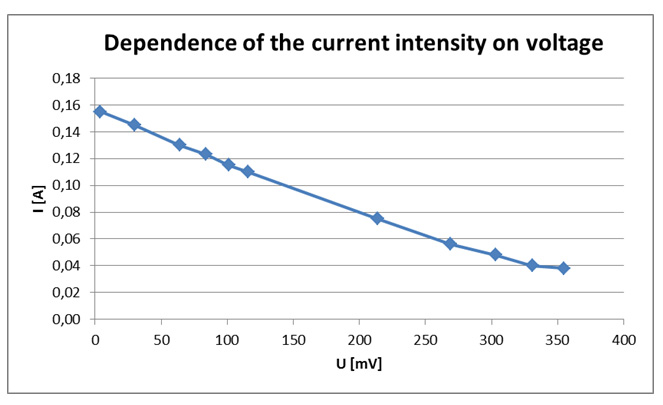
Figure IV.11. An example of the dependence of the current intensity on voltage for the working blueberry cell.
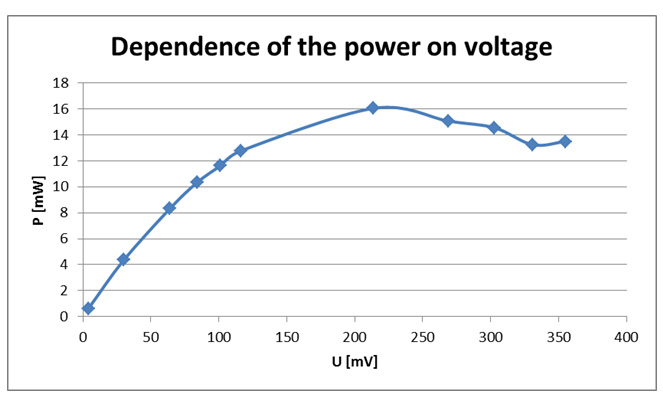
Figure IV.12. An exemplary dependence of the power on voltage for the working blueberry cell.
Discussion:
- Will the use of different fruit change the power of the device? (the possibility of an Activity al verification)
- How do the changes in resistance affect the cell power?
- Where can this type of the cell be applied?